Let’s assume that you have a SQL Server workload on Premises and want to take those to the cloud.
You have two options for MS SQL Server migration to aws.
The first option is a self-managed option which would be installing SQL Server on EC2 (Elastic Compute cloud).
To simplify, you get a virtual machine, you install MS SQL Server the way that you need based on your business requirements.
Amazon EC2 gives you complete control over every setting, just like when it’s installed on premises.
The second approach is running SQL Server on Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service).
Amazon RDS is a fully managed service that takes care of all the maintenance, backups, and patching for you.
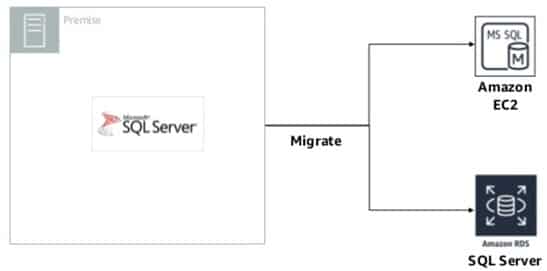
Figure 1 – Two Options of Migrating SQL Server Databases to AWS.
SQL Server on Amazon EC2
Using Amazon EC2 is like running a SQL Server database on premises. You have full control over the operating system, database installation, and configuration.
You are responsible for administering the database, patching the operating system and the database, tuning of the operating system and database parameters, managing security, backups, recovery, and configuring high availability or replication across your instances in the same or different regions.
With EC2, you can quickly provision and configure DB instances and storage, and you can scale your instances by changing the size of your instances or amount of storage.
You can provision your databases in AWS Regions across the world to provide low latency to your end users worldwide.
Running your own relational database on Amazon EC2 is the ideal scenario if you require a maximum level of control and configurability.
You can also use SQL Server services and features that are not available in Amazon RDS.
Amazon RDS for SQL Server
On the other hand, Amazon RDS is a fully managed service that makes it easier to set up, operate, and scale a relational database in the cloud.
RDS automates installation, disk provisioning and management, patching, minor and major version upgrades, backup and recovery of your SQL Server databases.
It also offers automated Multi-AZ (Availability Zone) synchronous replication, allowing you to set up a highly available and scalable environment fully managed by AWS.
It is offered in multiple database engines (PostgreSQL, Oracle, MySQL, Maria DB, SQL Server…). This is a managed service have some guardrails around.
For example, you don’t have:
- administrator access to the instance that is running SQL,
- you don’t have access to the filesystem,
- you can’t RDP to that server running SQL, etc.
- Also, there are features that are not supported by SQL Server AWS RDS, here you can see the ever-shrinking list.

Figure 2 – SQL Server Features on Amazon RDS vs EC2.
Choosing Between Microsoft SQL Server Solutions on AWS
For SQL Server databases, both Amazon RDS and Amazon EC2 have advantages and certain limitations.
Using RDS lets you focus on more important tasks, rather than the day-to-day administration of SQL Server and the underlying software stack.
Also, it can be more cost-effective than Amazon EC2.
Alternatively, Amazon EC2 gives you flexibility, more control, and choice.
In general, consider Amazon RDS first.
Based on your answers to the considerations preceding, Amazon RDS might be a better choice than Amazon EC2 if:
- You want to focus on high-level tasks, such as performance tuning and schema optimization, and outsource the following tasks to Amazon:
- management of security patches,
- upgrades of minor SQL Server versions,
- provisioning of the database,
- management of backup and recovery and
- storage management.
- You need a highly available database solution and want to take advantage of the push-button, synchronous Multi-AZ replication without having to manually set up and maintain database mirroring, AlwaysOn, Availability Groups or fail-over clusters.
However, running SQL Server on AWS EC2 might be the better choice if the following is true:
- You need full control over the DB instances, to the operating system and software stack.
- You require host access for SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) packages or bulk insert operations.
- You want to use third-party solutions or your own experienced database administrators to manage the databases, including backups, replication, and clustering.
- Your database size and performance requirements exceed the current maximums or other limits of Amazon RDS or need to use SQL Server features not currently supported by Amazon RDS.
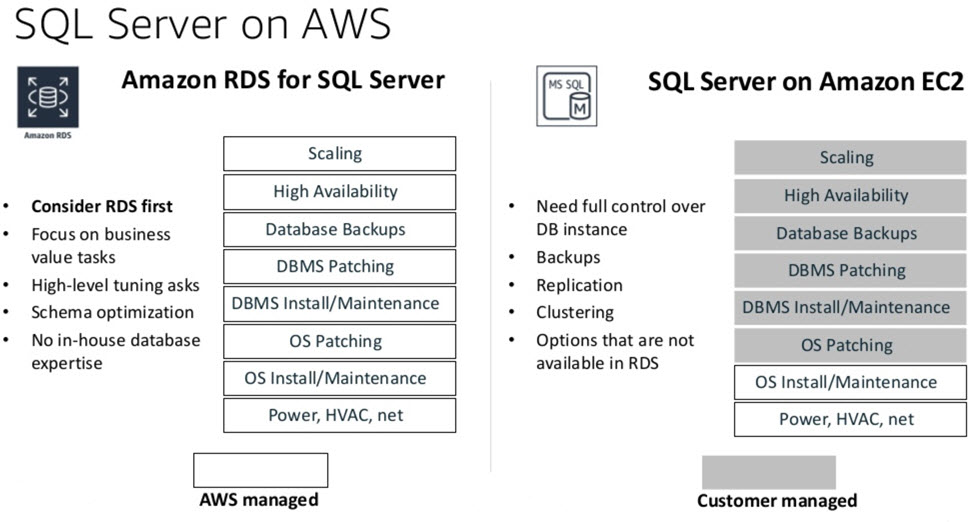
Figure 3- Differences between SQL Server RDS vs. EC2.
Assessment and planning (Best practices)
Inventory SQL Server all dependencies
There’s a lot of things that you need to correctly understand to make a successful SQL migration to AWS.
The first thing would be to inventory all your SQL Server dependencies.
Make sure that you know exactly which web servers are interfacing with your SQL Server, know that maybe there is a reporting service server running somewhere.
Know who is interacting with your systems. So, when it comes time for you migrate to aws, you will know exactly who’s going to be impacted and you can minimize the impact to these entities.
Identity SQL versions or edition features
Identity SQL Versions or edition features currently used.
This may be an opportunity for you to reduce your licensing costs.
Understand high viability and disaster recovery requirements and authentication requirements (windows authentication vs SQL) will help you decide which route to go: RDS or EC2.
Know your licensing options
Maybe you can bring your own SQL license, depending on the licensing agreement that you have with Microsoft. The options may vary so understanding it very well can save you a lot of money.
SQL Performance Requirements
Take performance requirements is important, especially if you want to show your stakeholders that the migration was a “Success”.
It means that you should baseline your existing environment, getting the performance reference points, so after the migration you can show that improve performance by X and availability by Y.
Leverage your retention policy
If you can leverage your retention policy, then we highly recommend that you do.
For example, assume that you have 10 years of data in SQL Server environment but your policy dictates for you to have five years.
Perhaps you should archive those five years that you don’t need into something like Amazon s3, which is cloud object storage service that is secure, persistent and cost-effective.
If you do it before the migration that would reduce your migration time and afterwards that could considerably save some money on performance costs.
Acknowledge Internal capabilities
When it comes to SQL migration time, the last thing would be to acknowledge your internal capabilities.
What does that mean? Let’s assume that your team is very tenured, they have the expertise in-house but maybe they don’t have the time or expertise to execute a migration.
If you need help with your SQL migration to AWS, bring in a partner (Red9 would be happy to help with your SQL Migration).
Hybrid Scenarios and Data Migration
Some AWS customers already have SQL Server running on-premises but want to use the AWS Cloud to enhance their architecture to provide a more highly available solution.
Other customers are looking to migrate workloads to AWS without incurring significant downtime.
AWS offers several services and an AWS SQL Migration tool to assist customers in these use cases, and SQL Server has several replication technologies that offer high availability and disaster recovery solutions.
These features differ depending on the SQL Server version and edition.
AWS storage solutions allow you to pay for only what you need. You get the benefits without the upfront investment and hassle of setting up and maintaining an on-premises system.
Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3)
S3 gives you the ability to back up SQL Server databases to a highly secure, available, durable, reliable storage solution.
Using Amazon S3, you can take advantage of the flexibility and pricing of cloud storage.
Many third-party backup solutions are designed to securely store SQL Server backups in Amazon S3.
Also, you can design and develop a SQL Server backup solution yourself by using AWS tools like the AWS CLI, AWS Tools for Windows PowerShell, or a wide variety of SDKs for .NET or Java, and the AWS Toolkit for Visual Studio.
AWS Storage Gateway
AWS Storage Gateway enables your existing on-premises–to–cloud backup applications to store primary backups on Amazon S3’s scalable, reliable, secure, and cost-effective storage service.
It is a service connecting an on-premises software appliance with cloud-based storage to provide seamless and secure integration between an organization’s on-premises IT environment and AWS’s storage infrastructure.
AWS Storage Gateway supports industry-standard storage protocols that work with your existing applications.
It provides low-latency performance by maintaining frequently accessed data on-premises while securely storing all your data encrypted in Amazon S3.
Native SQL Server migration methods
Amazon RDS also supports native migration methods.
These approaches extend your existing on-premises high-availability solution and provide a disaster recover solution with AWS by using the native SQL Server features like log shipping, database mirroring (Enterprise version), Always on Availability groups (SQL server 2014 or newer), distributed Availability groups (SQL Server 2016 or newer) and transaction replication.
AWS Snowball Edge
Snowball is a service and a physical storage appliance that enables you to move petabytes of data to AWS.
It helps eliminate challenges that you can encounter with large-scale data transfers, including high network costs, long transfer times, and security concerns.
You can order a book or a Crock-Pot on Amazon Prime, knowing it will show up at your door two days later.
Similarly, you can order several AWS Snowball Edge appliances from your AWS Management Console.
Once it arrives, attach the device to your local network, download and run the Snowball Client (“Client”) to establish a connection, and then use the Client to select the file directories that you want to transfer to the device.
The Client will then encrypt and transfer the files to the device at high speed.
Once the transfer is complete and the device is ready to be returned, the E Ink shipping label will automatically update and you can track the job status via Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS), text messages, or directly in the Console.
AWS Database Migration Service (AWS DMS)
You can begin a database migration with just a few clicks in the AWS Management Console.
It helps you migrate databases easily and securely. The source database remains fully operational during the migration, minimizing downtime to applications that rely on the database.
Once the migration has started, AWS manages many of the complexities of the migration process like data type transformation, compression, and parallel transfer (for faster data transfer) while ensuring that data changes to the source database that occur during the migration process are automatically replicated to the target.
DMS is intended to support migrations to and from AWS hosted databases, where both the source and destination engine are the same and heterogeneous data sources.

Figure 4 – Hybrid Scenarios and Data Migration.
Conclusion:
If you decided to migrate your SQL Server workload to AWS there are multiple ways to do it.
If any of it is too confusing or you have questions, please call us and we will walk you through your questions. (Even if you don’t hire us)
