RDS is a managed database service that will do all the heavy lifting that you normally must-do. It automates everyday database administration tasks like:
- Backup and restore
- Scaling
- Patching
- Upgrading the server
- High availability
- Failover support for DB instances using multi-AZ deployments that provisions and maintains a synchronous standby replica in a different Availability Zone (AZ).
The RDS service is built to free up DB administration time. And spend time doing things that are more beneficial for your end customers, like innovating.
Amazon RDS has multi-engine support, which means that you can run Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, Amazon Aurora, MySQL, MariaDB, and PostgreSQL.
Licensing MS SQL Server for AWS RDS
For MS SQL Server specifically, RDS supports different editions along with a couple of different license types. The service supports the “License Included” licensing model. If you have license mobility, you’re able to bring your license to RDS.

Amazon RDS for SQL Server
Amazon RDS for SQL Server permits use of cloud formation templates to launch new SQL Server instances scaling up or down between various instance types with storage from 100GB to 16 TB.
There’s a wide range of things that Amazon does within RDS for SQL Server that will make your life simpler. Adding high availability with AWS database mirroring, encryption, sync to Active Directory (AD) and do Windows Authentication.
Scale Storage
Microsoft collaborated with customers and the number complaint was that most everybody has been asking is scaling storage on RDS for SQL Server.
In the past you had to figure out how much storage you wanted, provision that amount and you could not change it. Recently online storage scaling was launched but with couple of limitations.
AWS RDS Storage Scaling Limitations
- When you issue a scale storage command to RDS SQL Server, the instance will go into a state called “storage optimizing”. During that period, you’re not allowed to do another scale storage operation until the last one completes.
- Scale storage does require a single EBS Volume. Older instance may have been created with more than one. Magnetic storage uses more than one volume too, so it doesn’t allow you to scale.

Instance Types
RDS provides a selection of instance types optimized to fit different relational database use cases.
Instance types comprise varying combinations of CPU, memory, storage, and networking capacity and give you the flexibility to choose the appropriate mix of resources for your Amazon database.
Each instance type includes one or more instance sizes, allowing you to scale your resources to the requirements of your target workload.
The newest AWS M5 instance type
The newest M5 Instances type is the next generation of the Amazon EC2 General Purpose compute instances. It offers a balance of computing, memory, and networking resources for a broad range of AWS DB database workloads. The M5 instances are powered by 2.5 GHz Intel Xeon scalable CPU and deliver improved price/performance compared to M4 instances.
M5 instances introduce a new larger-sized model: m5.24xlarge.
Here you get:
- whopping 96 vCPUs;
- 384 GB of RAM;
- next-generation Elastic Network Adapter (ENA) and
- NVM Express (NVMe) technology provides to offer up to 25 Gbps of network bandwidth and up to 10 Gbps of dedicated bandwidth for database storage.
More info here.
Amazon RDS Licensing for SQL Server
You can choose from two licensing models:
- License Included or
- Bring Your Own License (BYOL).
In the BYOL model, you provide your own license under the Microsoft License Mobility program.
License Included model is held by AWS and is included in the Amazon RDS instance price.
Amazon offers SQL Server Enterprise Edition License Included in all AWS commercial regions (non-governmental regions) and on additional instance types:
- R3,
- M4 and
- M5 with a minimum of 4 vCPUs.
You don’t need separately purchased SQL Server licenses.
Pricing includes the software license, the underlying hardware resources and all database management capabilities.
Simply launch a SQL Server Enterprise Edition instance in the AWS Management Console and select the License Included option.
For more information about AWS RDS pricing, see this: https://aws.amazon.com/rds/sqlserver/pricing/
SQL Server High Availability
SQL Server DB instances use SQL Server Mirroring to provides high availability and failover support for DB instances using multi-AZ deployments.
The primary DB instance is synchronously replicated across Availability Zones to a standby replica to provide data redundancy, eliminates I/O freezes, and minimize latency spikes during system backups.
Running a DB instance with high availability can enhance availability during planned system maintenance and help protect your databases against DB instance failure and Availability Zone disruption.
More about AWS AZ:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/UserGuide/Concepts.RegionsAndAvailabilityZones.html
Windows Authentication Support
You can enable Windows Authentication when creating a new database or add it to an existing database.
Credential information should be stored in the AWS Directory Service for Microsoft Active Directory (AD).

Amazon RDS, SQL Server and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
You can use Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) to encrypt connections between your client applications and your Amazon RDS DB instances running Microsoft SQL Server.
SSL support is available in all AWS regions for all supported SQL Server editions.
When you create a SQL Server DB instance, Amazon RDS creates an SSL certificate for it.
The SSL certificate includes the DB instance endpoint as the Common Name (CN) for the SSL certificate to guard against spoofing attacks.
There are two ways to use SSL to connect to your SQL Server DB instance:
- Use force SSL for all connections (this happens transparently to the client, and the client doesn’t have to do any work to use SSL) or
- Encrypt specific connections (this sets up an SSL connection from a specific client computer, and you must do work on the client to encrypt connections).

Figure 5 – RDS for SQL Server (Forced TLS/SSL).
HIPAA Eligibility for Amazon RDS for SQL Server
The AWS Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) compliance program have been expanded to include Amazon RDS for SQL Server.
All Amazon RDS database engines are now HIPAA-eligible.
RDS can be used to build HIPAA-compliant applications and store healthcare related information, including protected health information (PHI) under an executed Business Associate Agreement (BAA).

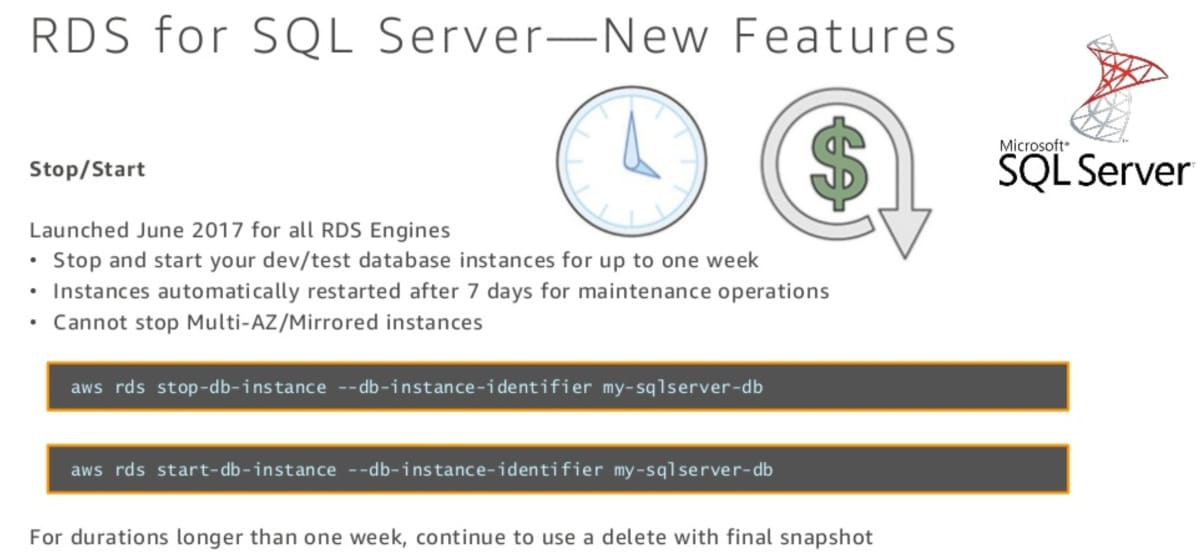
Stop/Start Operation
The stop/start feature is available for database instances running in a Single-AZ deployment, which are not part of a Read Replica (both source and replica) configuration.
Amazon RDS for SQL Server allows you to quickly stop and start your DB instances that are not required to be running all of the time (DBS for test and dev).
While your database instance is stopped, you are charged for provisioned storage, manual snapshots and automated backup storage within your specified retention window, but not for db instance hours.
You can stop an instance for up to 7 days at a time. After 7 days, it will be automatically started.

All pretty exciting features. So, there you have it.
This is what Amazon RDS for Microsoft SQL Server today looks like.
Additional Information:
- SQL Server migration to Amazon RDS best practices (AWS migration)
- SQL Server on Amazon RDS – Availability best practices
- Microsoft SQL Server migration strategies to AWS
