4 Ways to Check SQL Server ERRORLOG Location
You can check sql error log path in a few ways:
1. Use TSQL
2. Use SQL Configuration Manager
3. Use EventViewer
4. Registry
1. Using TSQL
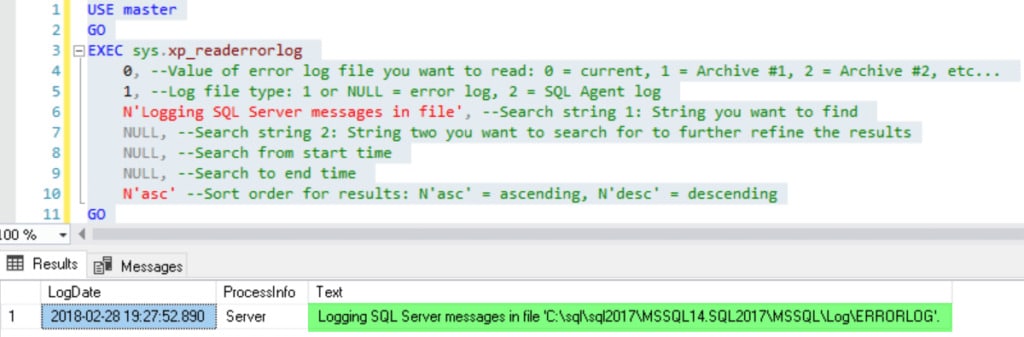
Find the sql server errorlog location setting:
USE masterGOEXEC sys.xp_readerrorlog
0, --Value of error log file you want to read: 0 = current, 1 = Archive #1, 2 = Archive #2, etc...
1, --Log file type: 1 or NULL = error log, 2 = SQL Agent log
N'Logging SQL Server messages in file', --Search string 1: String you want to find
NULL, --Search string 2: String two you want to search for to further refine the results
NULL, --Search from start time
NULL, --Search to end time
N'asc' --Sort order for results: N'asc' = ascending, N'desc' = descending
The result should be:
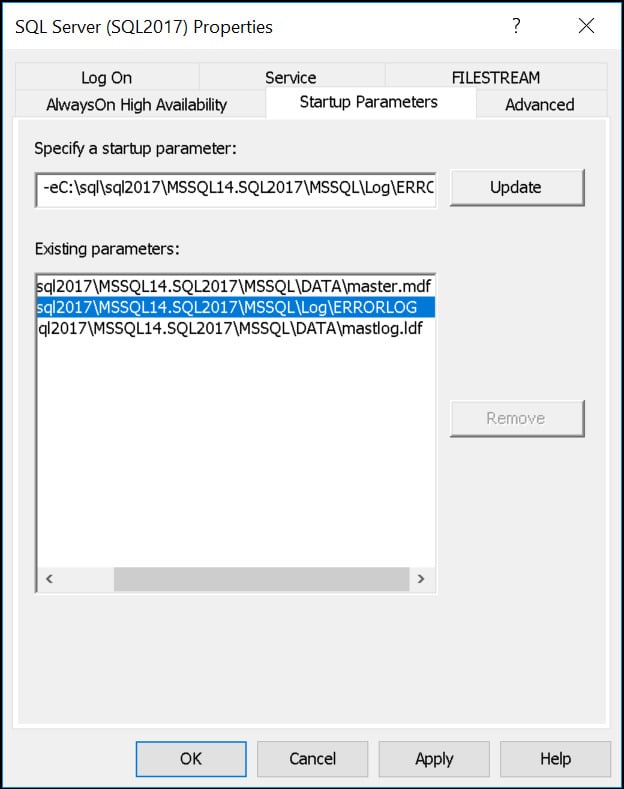
2. SQL Configuration Manager
Accessing SQL Server Configuration Manager
- Go to “SQL Server Services”;
- Click on SQL instance on the right. (In my case its “SQL2017”);
- Right-click, go to Properties.
- Look for “Startup Parameters” tab.
One of “Existing parameters” shows the ERRORLOG path.
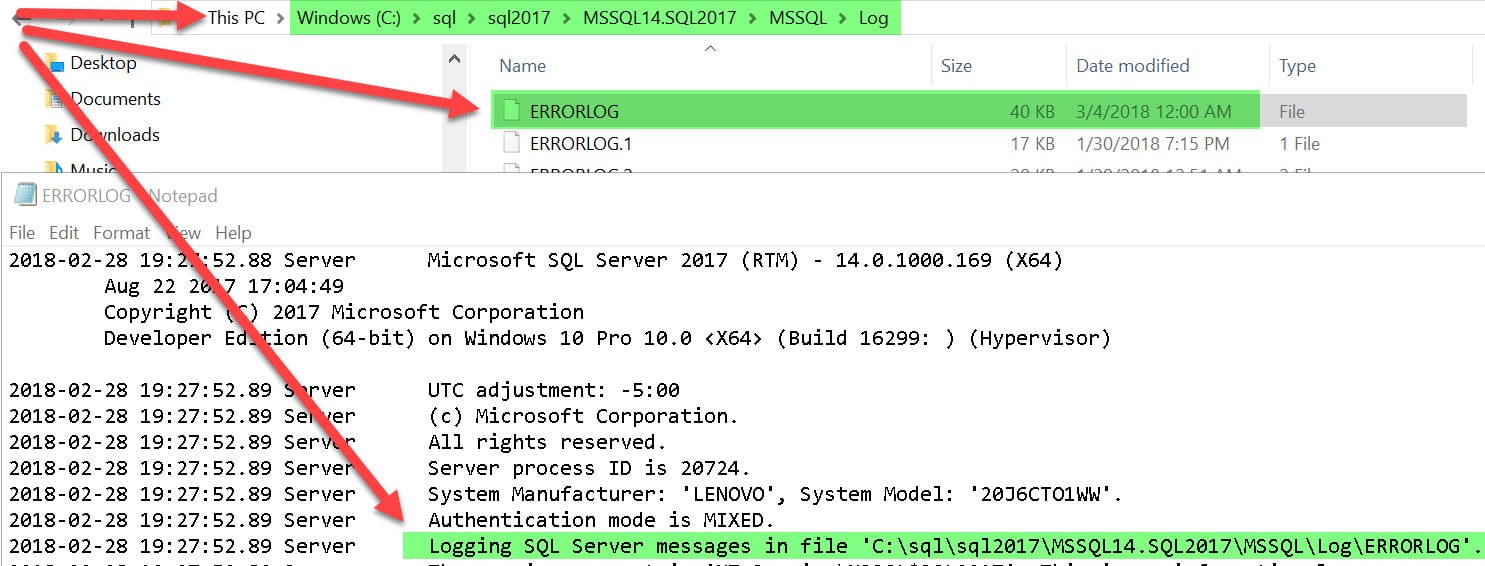
Here are SQL Server logs location on my laptop:
3. Using EventViewer
Start the EventViewer (you can use the search box near the Start button).
- Click on the Windows Logs > Application > Filter Current Log.
- Replace <All Event IDs> with EventID 17111 and hit OK.



4. Using Registry
Are you serious? Are you going to try to look up the path using the registry? Yeah, it is possible.
You have three methods above to do this. I do not see a good reason to go the registry route, but in case you must, here it is:

To change or move the ERROLOG path, I do this using SQL Configuration Manager, change parameter “-e”. Restart the SQL Service.
Warning: if directory does not exist or SQL Server Service does not have enough permissions, SQL Engine will not start.
You will most likely get “The request failed or the service did not respond in a timely fashion….” error.
To check SQLAgent ERRORLOG location, go to SQL Server Management Studio > SQL Server Agent > right-click “Properties”.

To change SQL Agent ERRORLOG, just run this:
USE msdbGOEXEC msdb.dbo.sp_set_sqlagent_properties @errorlog_file=N'<New_Errorlog_Path>\SQLAGENT.OUT'
GO
